RF CO2 vs. Glass CO2
RF laser cutting machines and glass laser cutting machines are both based on CO2 laser technology, but they differ in their laser source design, beam characteristics, power and efficiency, and overall performance. Here are their main features and differences.
RF CO2
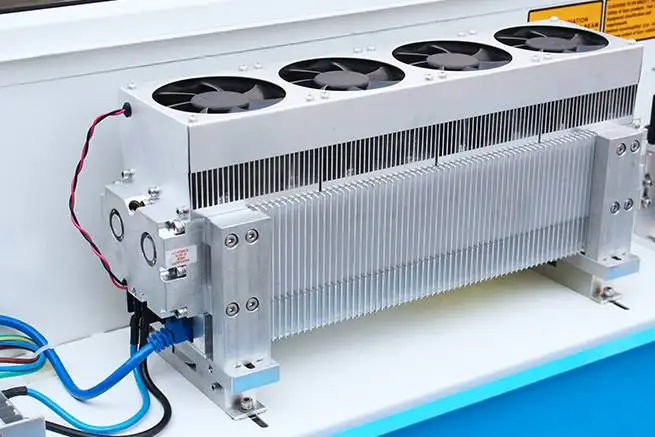

Laser Source
This laser source is powered by an RF generator, which excites the gas mixture (typically CO2, N2, and He) to produce laser radiation.
Beam Characteristics
The laser beam produced by an RF laser source has a high-quality Gaussian beam profile, which allows for precise and consistent cutting quality.
Power and Efficiency
RF laser sources can achieve high output powers, typically ranging from hundreds of watts to several kilowatts. They also offer relatively high electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency, resulting in lower operating costs.
Material Compatibility
RF laser cutting machines can process a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, ceramics, and composites, making them versatile tools for various industrial applications.
Advantages
RF laser sources are known for their long operational lifetime, low maintenance requirements, and high beam quality. They can achieve precise cuts with narrow kerfs and offer excellent cutting speeds, especially for non-metallic materials.
Limitations
RF laser cutting machines can be more expensive than conventional CO2 laser systems due to the additional RF generator and associated components.
Glass CO2
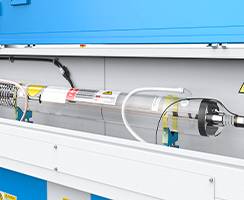
Laser Source
The laser beam is generated within a sealed glass tube filled with a gas mixture (typically CO2, N2, and He).
Beam Characteristics
The laser beam produced by a glass laser source has a relatively good beam quality, but it may not match the Gaussian beam profile of RF laser sources.
Power and Efficiency
Glass laser sources can achieve moderate output powers, typically ranging from several tens of watts to a few hundred watts. Their electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency is generally lower than RF laser sources.
Material Compatibility
Glass laser cutting machines can process a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics, but they may not be as efficient as RF laser sources for certain applications.
Advantages
Glass laser sources are relatively simple in design and can be more cost-effective than RF laser sources for lower power applications. They offer a balance between performance and cost, making them suitable for many industrial cutting applications.
Limitations
Glass laser sources have a shorter operational lifetime compared to RF laser sources, and they may require more frequent maintenance or replacement. Additionally, their beam quality and efficiency may not be as high as RF laser sources.
Summary
RF laser sources offer higher output powers, better beam quality, higher efficiency, and longer operational lifetimes, but they can be more expensive. Glass laser sources, on the other hand, provide a balance between performance and cost, making them suitable for many industrial cutting applications where moderate power levels are sufficient.
The choice between the two depends on factors such as the required cutting performance, material compatibility, budget constraints, and specific application requirements.

.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Česká
Česká
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Romania
Romania
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa