Laser etching has revolutionized how we personalize and mark materials with precision. By using a focused laser beam, intricate designs can be created on a variety of substrates, including metal, glass, and leather.
This technique offers numerous advantages, such as durability, high detail, and speed. As industries continue to embrace this technology, understanding the key aspects of laser etch is essential for achieving optimal results, whether for industrial applications or custom items.

1. What is Laser Etching?
Laser etching is a marking technique that uses a concentrated laser beam to alter the surface of a material. It typically affects only the top layer of the material. The laser’s heat either vaporizes a portion of the material or causes a discoloration, resulting in a shallow, precise mark.
Laser etch is widely valued for its accuracy, durability, and non-invasive nature, as it typically does not damage the underlying material. The process relies on the controlled application of heat, allowing for high precision without significantly altering the material’s structure.
2. Laser Etching vs. Laser Engraving: What’s the Key Difference?
2.1. Laser Etching
Laser etching is a surface-level process. The laser affects only the top layer of the material, creating a shallow, often raised or discolored mark. This process is ideal for applications where only a thin, surface-level design or text is needed, such as branding or decorative marks.
Laser Etching is commonly used for branding, decorative designs, or text on materials such as metals, glass, and plastics. Typically, UV or fiber lasers are used for etching, depending on the material. It is ideal for projects that require a light, permanent mark without penetrating deep into the material.

2.2. Laser Engraving
Laser engraving involves removing material to create a deeper mark with a laser engraver. This technique is typically used for more durable, high-contrast markings and is ideal for applications that require more pronounced designs or patterns.
The most common types of lasers used in engraving are CO₂ lasers, ideal for wood, acrylic, and leather; fiber lasers, which are best suited for metals and some plastics; and diode lasers, commonly used for smaller projects on lighter materials like wood and paper. The depth of the engraving can vary, but it generally results in a more noticeable indentation compared to laser etching.

3. Types of Lasers Used in Etching
3.1. Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers are among the most widely used lasers in etching, especially for metals. Operating with a wavelength of 1064 nm, they are highly effective at etching materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. The wavelength of fiber lasers is more readily absorbed by metals, which allows them to produce sharp, precise, and permanent marks with high contrast.
These lasers are known for their ability to etch intricate details and fine text, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision, such as serial numbers, logos, and barcodes. Fiber lasers can etch deep, durable marks without compromising the integrity of the material.
3.2. UV Lasers
UV lasers emit a shorter wavelength of light, which allows them to focus on very small areas with great accuracy. They are ideal for etching delicate materials or those that are sensitive to heat, such as glass, plastics, and certain coatings.
UV lasers are known for their small spot size and exceptional precision, which makes them ideal for detailed etching. However, However, they are more commonly used for non-metallic materials, as their shorter wavelength is less effective for penetrating metal surfaces compared to fiber lasers.
Depending on the focus of your projects, you can determine the laser type and choose a high-quality laser etching machine that suits your needs.
4. What Materials Can You Etch with Lasers?
4.1. Laser Etching Metal
Metal etching is one of the most common applications of laser etching. Laser etching stainless steel, laser etching aluminum, brass and titanium are often used to create detailed markings, logos, and serial numbers.
Laser etching on metal creates a permanent, wear-resistant mark that won’t fade or rub off. This makes it ideal for identifying parts, marking products for traceability, and creating custom designs on metal products.
The process is particularly useful in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where durability and precision are essential.

4.2. Laser Etching Glass
Laser etching on glass is commonly used for creating custom designs, logos, or text on products like wine glasses, trophies, and decorative items. The laser’s heat can etch the surface of the glass, leaving behind a contrasting mark that can range from subtle patterns to detailed logos.
Glass etching is popular for both consumer and corporate applications. The precision of the laser allows for fine details and intricate designs to be created on the glass surface, resulting in unique, personalized items.

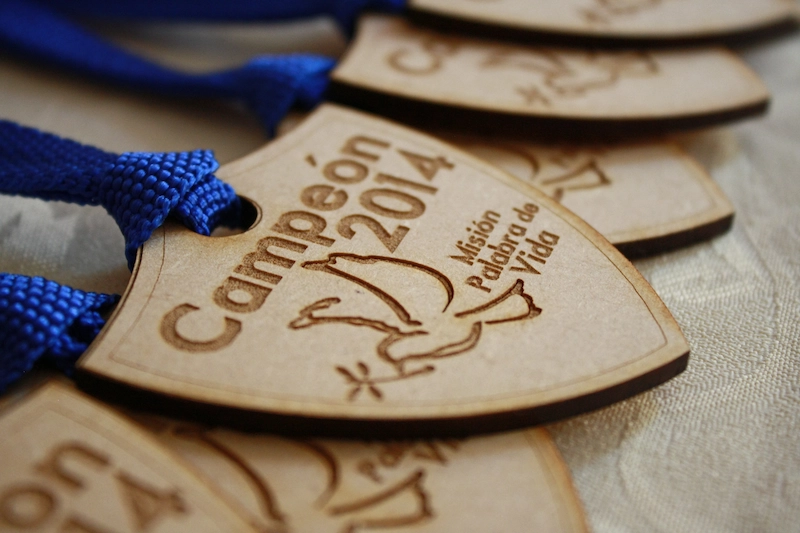
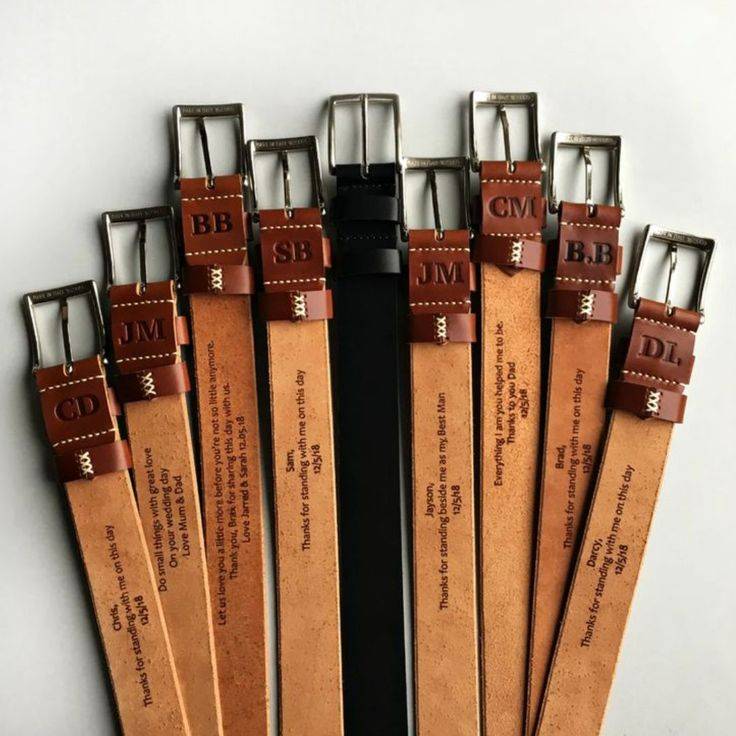
4.3. Laser Etching Leather
Laser etch is a popular method for personalizing leather items such as wallets, belts, and bags. The process works by using the laser’s heat to burn the surface of the leather, creating a darkened mark that contrasts beautifully with the natural color of the material.
Laser etching onto leather is a great way to add logos, monograms, or decorative patterns to leather products. It is also highly durable, ensuring that the designs remain intact even after years of use.

5. Applications of Laser Etching
- Manufacturing: Used to mark serial numbers, part numbers, and logos on components.
- Consumer Goods: Items such as jewelry, gifts, and accessories are often laser-etched for personalization.
- Medical Devices: Marking surgical tools, implants, and medical devices with serial numbers or identification marks.
- Electronics: Marking serial numbers, logos, and barcodes on electronic components and devices.
6. Does Laser Etching Wear Off?
No, laser etch creates permanent marks that do not wear off, fade, or peel under normal conditions.
Because the laser creates marks by either vaporizing a portion of the material or chemically altering it, these marks are deeply embedded in the surface and do not fade over time. Unlike printed or painted marks, which can wear off or peel, laser-etched designs are resistant to the elements and wear.
However, the durability of laser etched markings can depend on the material being etched. For example, metal surfaces such as stainless steel or aluminum tend to hold etched marks for a long time, while softer materials like wood or leather may show signs of wear after extended use. Regardless, laser etching remains one of the most permanent marking methods available.
7. How to Choose the Right Laser Etching Machine?
Choosing the right laser etching machine depends on several key factors, including the type of material you plan to work with, your budget, and the specific needs of your projects. The ideal machine should align with your production goals, ensuring precision, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
For those primarily etching metals like stainless steel or aluminum, a fiber laser is an excellent choice. Fiber lasers are known for their ability to produce high-precision, deep marks on metals, making them ideal for industrial and manufacturing applications where durability is essential.
When selecting a laser etch machine, it is important to consider the power, speed, and precision of the laser. The laser’s power affects the depth and speed of the etching process, with higher wattage machines able to produce deeper marks more quickly. Speed is particularly important for businesses with large-scale production needs, as it directly impacts workflow efficiency. Precision is key for intricate designs, logos, and text, ensuring that every etch meets high standards of clarity and detail.
The machine’s features should also be evaluated, including its ease of use, software compatibility, and additional accessories. User-friendly interfaces and advanced software allow for easy design imports, precise control over etching settings. The durability and maintenance should also be considered. Machines that require less frequent maintenance will reduce downtime and overall operational costs in the long run. Besides, laser machines equipped with a rotary attachment can increase project versatility, enabling etching on curved surfaces such as tumblers and rings.
For businesses focused on productivity and long-term growth, the Aurora Etching Laser Machine is an excellent option. Being a business-level high-precision laser etching machine, the Aurora allows you to choose between a UV or fiber laser configuration based on your specific needs.
The Aurora delivers high efficiency, fast etching speeds, and high-precision results, while its durable build ensures continuous operation. With an intuitive interface and advanced features, the Aurora is a valuable asset for companies looking to increase output with a steady high quality.
Conclusion
FAQs About Laser Etching
Is laser etching permanent?
Is laser etching permanent?
How deep does laser etching go?
How deep does laser etching go?
How much does a etching laser machine cost?
How much does a etching laser machine cost?
The cost of a etching laser machine varies widely, ranging from around $500 for entry-level models to over $10,000 for industrial-grade machines, depending on the features, power, and material compatibility.
If you’re looking for an affordable yet reliable option, Thunder Laser offers high-end laser machines that balance cost and performance, a great choice for businesses or hobbyists seeking high-quality etching without the hefty price tag.


.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Česká
Česká
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Romania
Romania
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 ジャパン
ジャパン
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa