Overview Of Laser Cutting
1. Principle of laser cutting
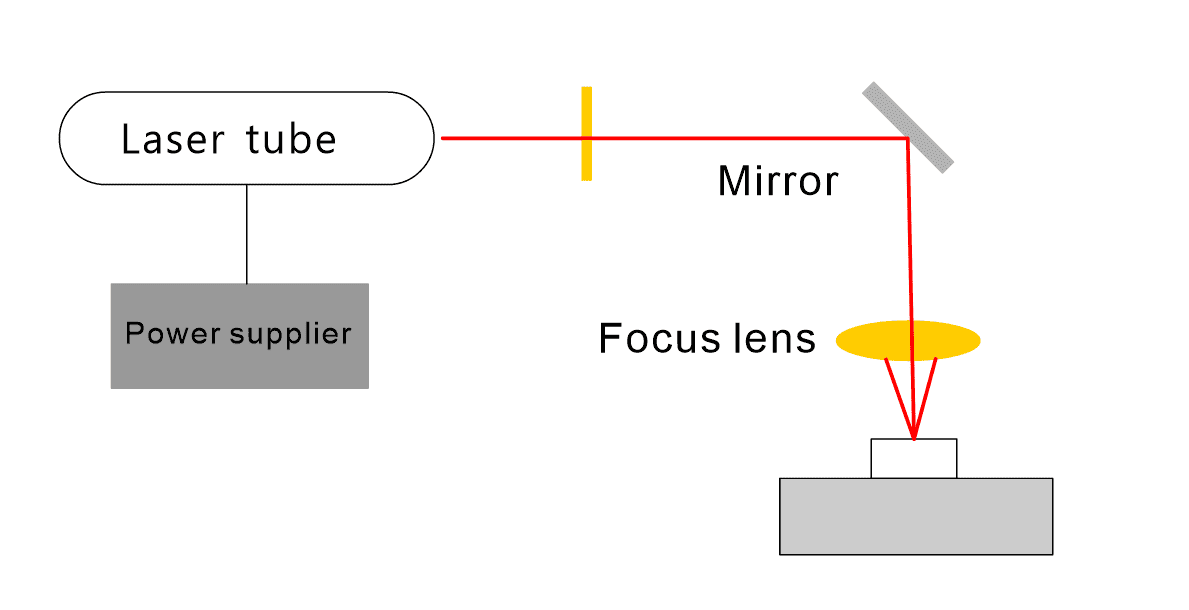
Laser cutting uses a high-power and high-density laser beam to irradiate the workpiece to melt, gasify and break it to cut the material, as shown in the figure.
2. Classification of main modes of laser cutting
Laser cutting is a versatile technology that offers various cutting modes to suit different materials and applications. These modes can be broadly categorized into the following:
(1) Gasification cutting
In gasification cutting, high-energy and high-density laser beams are utilized to heat the workpiece rapidly. This intense heat elevates the surface temperature of the material to its boiling point. Consequently, part of the material is vaporized, while another portion is expelled from the bottom of the cutting seam through the assistance of auxiliary gases. This process results in the removal of material and forms the cut. Gasification cutting is primarily employed for cutting brittle metal materials and select non-metallic materials, including wood, carbon materials, plastics, and rubber. For instance, the Thunder Laser Nova series laser cutter predominantly employs this method due to its effectiveness on these materials
(2) Melt cutting
Melt cutting involves the application of a high-energy and high-density laser beam to heat the workpiece to the point of material melting. Simultaneously, a high-pressure, non-oxidizing gas, such as Argon (Ar), Helium (He), or Nitrogen (N), is blown through a nozzle to remove the molten material and create a material incision.
Melt cutting is particularly suitable for materials that are less prone to oxidation or active metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and their respective alloys.
(3) Oxidizing, melting, and cutting
This mode utilizes a high-energy and high-density laser beam as a preheating heat source. Concurrently, a nozzle directs high-pressure oxygen or other active gases onto the material as cutting gases. This approach serves a dual purpose: first, the high-pressure oxygen reacts with the cut metal, generating significant oxidation heat; second, the molten oxide and melt are expelled from the reaction zone, resulting in a material cut.
Oxidizing, melting, and cutting are commonly employed for easily oxidizable metal materials, including carbon steel, titanium steel, and heat-treated steel.
(4) Control fracture cutting
Controlled fracture cutting is employed on brittle materials, inducing a large thermal gradient and severe mechanical deformation using a high-energy and high-density laser beam. This process forms a minor groove through thermal evaporation. Subsequently, external force is applied to initiate fracture along the minor groove, creating a material notch. This mode is particularly useful for scribing ceramics and wafers, where precise control over the fracture process is essential.
Overview Of CO2 Laser Cutting Machine System Composition
1. Overall structure of CO2 laser cutting machine
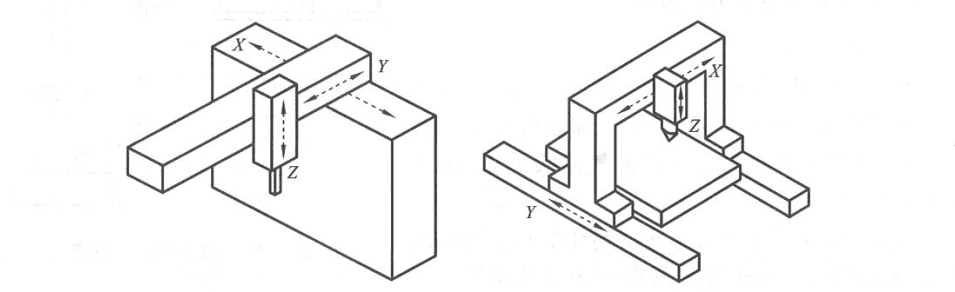
According to the relative movement of the laser cutting head and the worktable, the CO2 laser cutting machine has three types:
- 1. Fixed Beam (Fixed Optical Path): In this configuration, the cutting head remains stationary while the worktable moves along the X and Y axes.
- 2. Mobile Beam (Flying Optical Path): Here, the cutting head moves along the X and Y-axis directions, while the worktable stays fixed. This setup is suitable for larger processing sizes and space-saving.
- 3. Hybrid Visual Approach (Semi-fixed and Semi-mobile Hybrid): This approach combines elements of both fixed and mobile configurations, offering versatility in precision and adaptability
(1) Beam fixation: During the cutting process, the beam fixation
The cutting head of the cutting machine can not move, and the position of the worktable moves along the X and Y axes, as shown in the figure.
(2) Beam movement: During the cutting process, the beam movement
The cutting head of the cutting machine moves along the X and Y axis directions, and the position of the worktable is fixed, so the processing size is large, and the equipment occupies a small area. The workpiece does not need to be clamped, which is the mainstream cutting machine model.
2. Laser Source for CO2 laser cutting machine
| Laser Source | Wavelength (μm) | Materials | Advantages | Disadvantages | Market Positioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser | 10.6 | Wood, acrylic, PP, plexiglass, | Excellent section quality | Expensive, high maintenance cost, high operation cost | 30-130W for non-metallic cutting and engraving, 500-20,000W for metal cutting, Thunder Laser focuses on non-metallic cutting |
| Fiber Laser | 10.6 | Metal,Plastic,Leather | Precision cutting, flexibility, suitable for thin sheets | Expensive, challenging with highly reflective materials like aluminum and copper, slow for thick plates | 30-100W for metal marking and high-precision cuts in thin materials. 1000-20,000W for metal cutting |
| YAG Solid-State | 1.06 | Metal materials | Cost-effective, cuts non-ferrous metals | Limited to materials below 8mm thickness, low cutting efficiency | Cutting metal materials with thickness below 8mm |

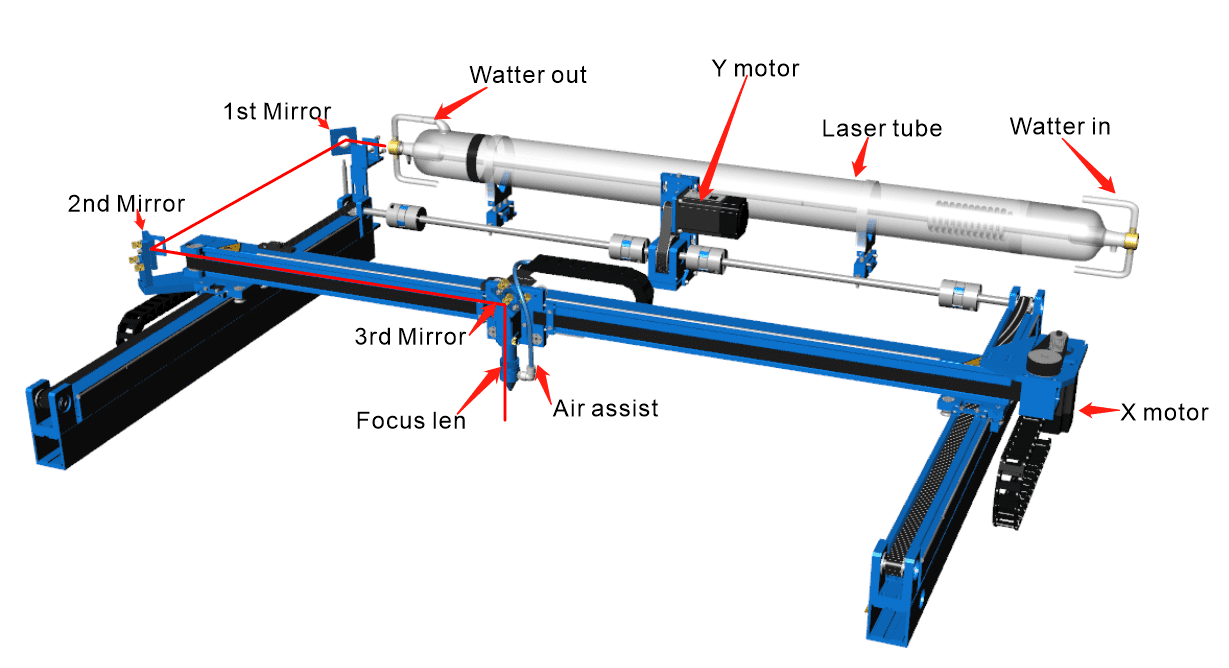
3. Laser light guiding and focusing system for CO2 laser cutting machine
The laser beam guidance and focusing system is a critical component of CO2 laser cutting machines, responsible for directing and concentrating the laser beam accurately onto the workpiece. Here, we’ll break down its function and composition in simpler terms:
(1) Function of laser light guide and focusing system:
When we use lasers for cutting or engraving, precision is key. The laser beam guidance and focusing system have a crucial role:
- Guiding the Laser Beam: It steers the laser beam to the right spot on the workpiece based on processing conditions, the shape of the workpiece, and the cutting or engraving requirements.
- Focusing the Laser Beam: It concentrates the laser beam to a fine point, ensuring it has the power to cut or engrave effectively.
(2) Composition of laser light guide and focusing system:
Now, let’s take a look at what makes up the laser beam guidance and focusing system, especially in a small CO2 laser cutting machine:
- Light Guide System: This part includes totally reflecting mirrors. Think of these mirrors like traffic signs for the laser beam. They bounce the laser light in the right direction, guiding it where it needs to go.
- Focusing System: This system consists of focusing mirrors. Imagine these mirrors as magnifying glasses for the laser beam. They converge the laser light to a tiny, powerful point, so it can cut or engrave precisely.
4. laser cutting system
(1)Control system composition:
The main control objects of the CO2 laser cutting machine control system contains the laser, the stepper motor driver in the movement mechanism, the blowing and exhaust fan and the chiller, as shown in the figure.
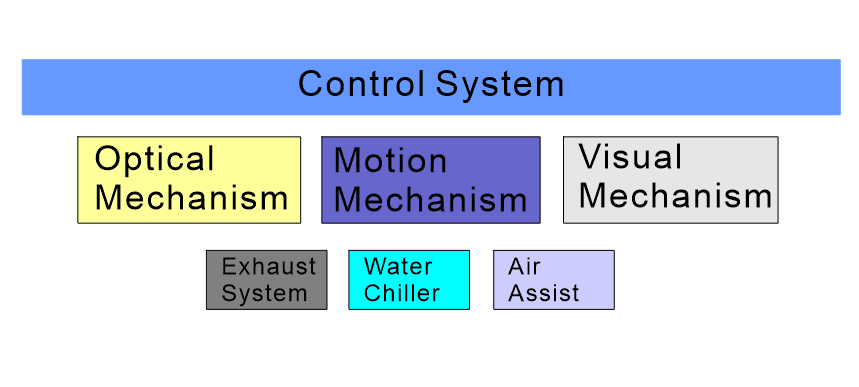
(2) Control system software and hardware composition:
the control system hardware comprises an industrial personal computer, control panel, main control card, interface board, driver, stepping motor, etc.
(3) The central controller works:
The central controller receives the operation and control commands from the computer and the panel to complete the work of controlling the operation of the motor, controlling the laser generation system, and monitoring and prompting various control States.
(4)Hardware composition of control system:
The control panel includes start, laser high voltage, reset, manual light output, pause, direction and other buttons as well as status indicator and laser energy regulator.
The control system software supports PLT, BMP and DXF file formats generated by various general graphics software, and adopts a mixed working mode of vector and dot matrix to complete engraving and cutting work.
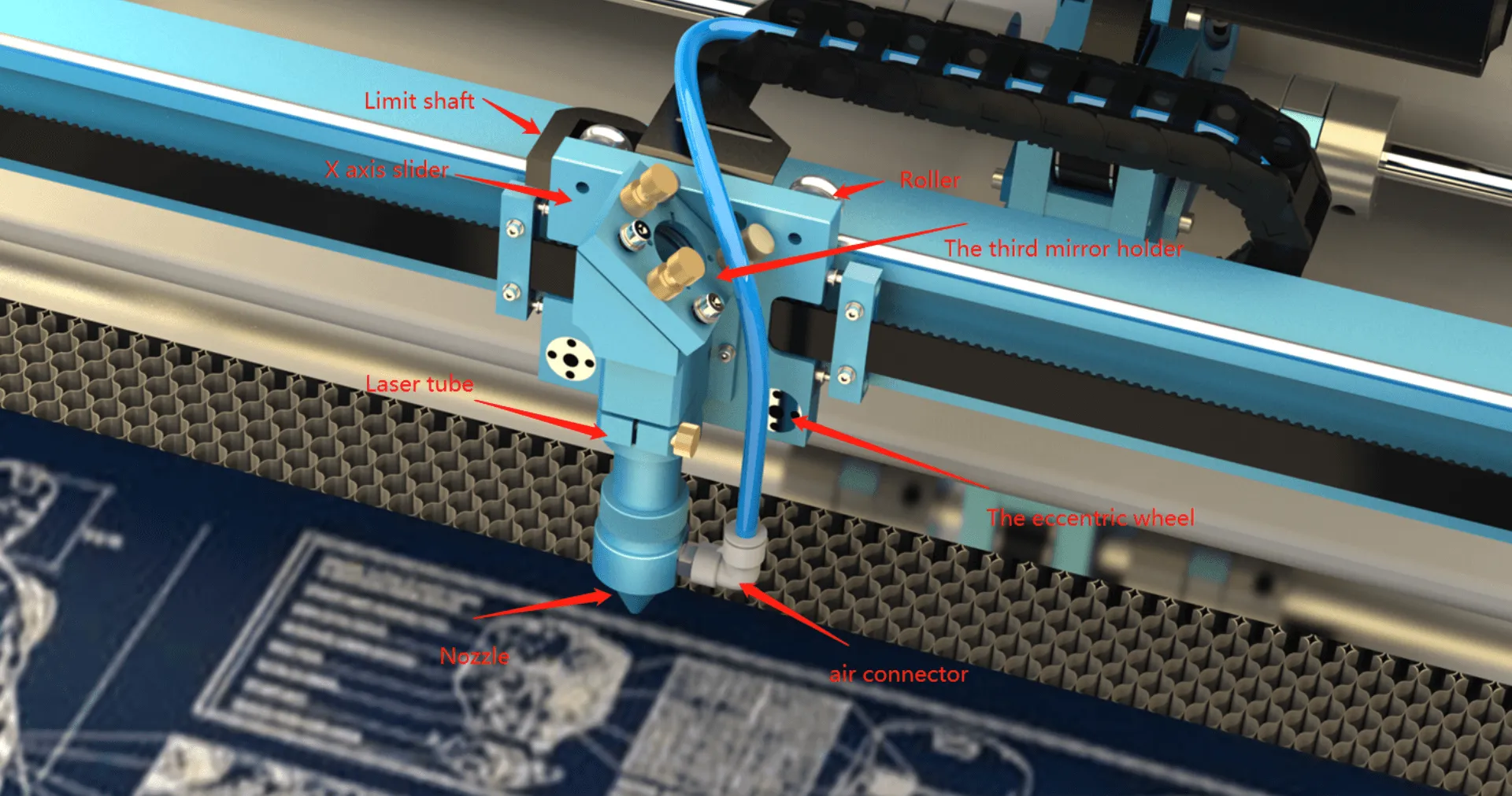
5. CO2 Laser cutting machine sensing and detection system case
The positive and negative stroke limit system of X-axis is as shown in the figure.
6. CO2 Laser cutting machine cooling and auxiliary system
The CO2 laser cutting machine’s cooling and the auxiliary system comprises cooling accessories such as an exhaust fan, blowing pump, water chiller, and cutting platform.
(1) Cutting platform:
There are two types of cutting platforms. The honeycomb platform is suitable for processing cloth, leather, and other soft materials, as shown in the figure; the other is the blade platform, ideal for processing plexiglass, thick plates, and other hard materials, as shown in the figure.

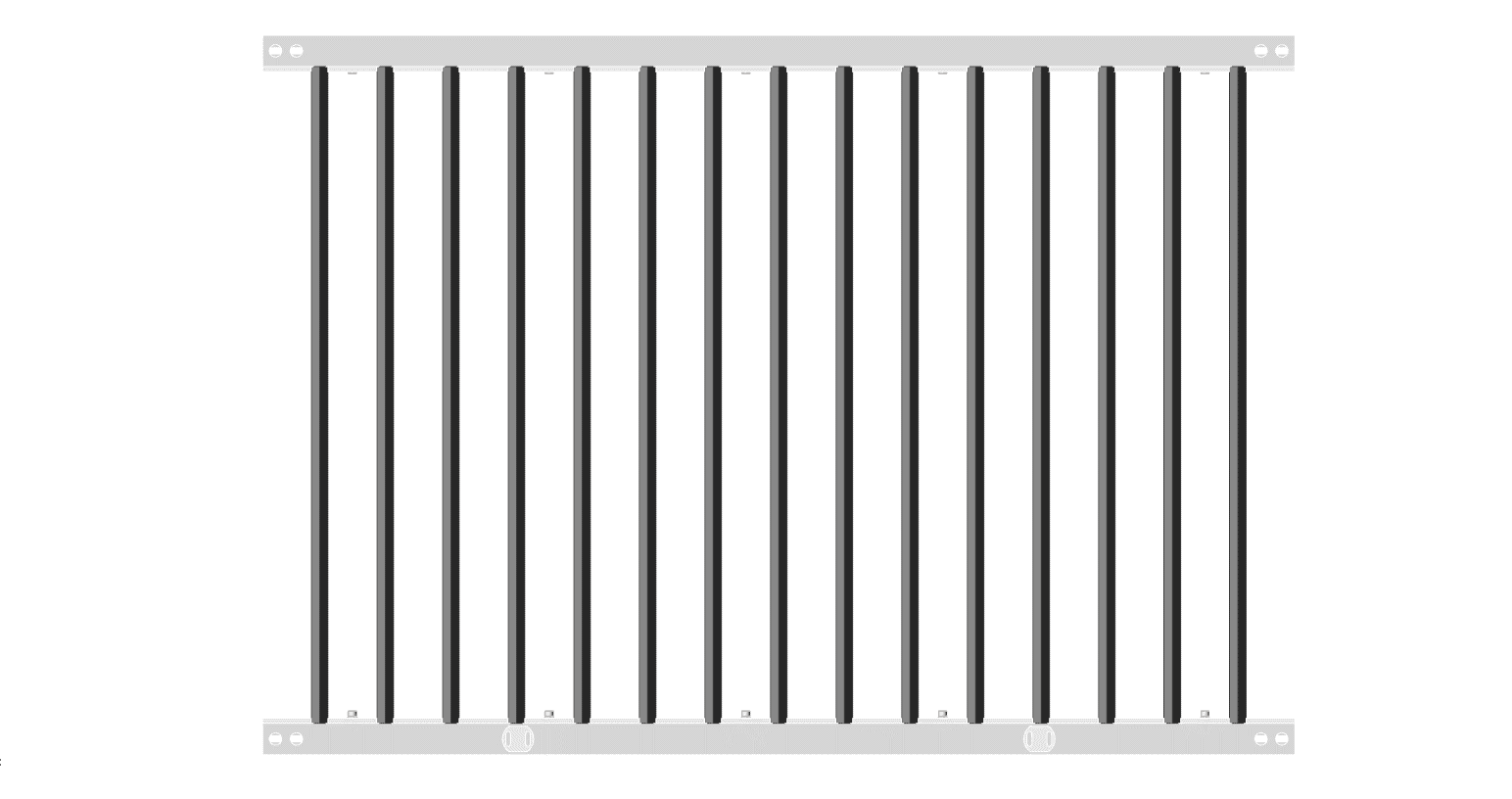
As shown in the figure. Some equipment with high adsorption requirements has vacuum adsorption platforms.

.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Mexico
Mexico
 Česká
Česká
 Romania
Romania
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 ジャパン
ジャパン India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa