- Author: Cathy
What is laser engraving?
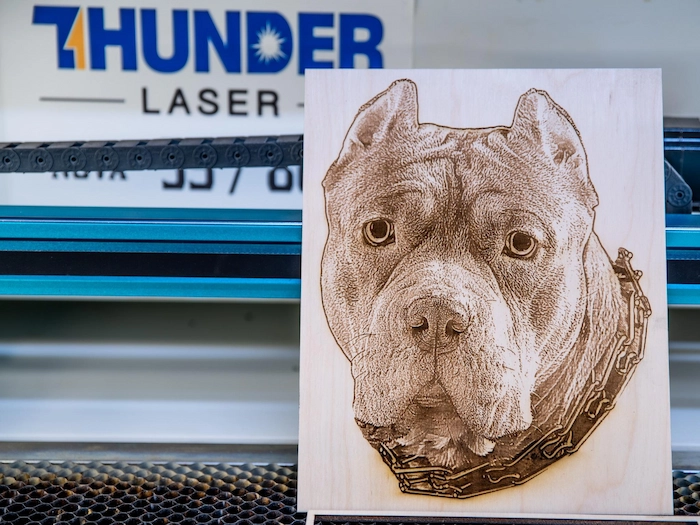
Laser engraving is a process that uses focused laser beams to etch or carve designs, text, or images onto various materials, including metal, wood, glass, plastic, and more materials. During this process, the laser vaporizes the material’s surface, creating a permanent mark that can range from fine, detailed artwork to deep, bold engravings.
Laser engraving is fast, requires minimal setup, and works with many materials, making it versatile for both creative and functional applications.
Is Laser Engrave Difficult?
Laser engraving is easier to get started with than many people think, thanks to user-friendly software, presets, and straightforward machine interfaces. However, mastering it can take some practice, especially when learning about the best settings for different materials, like adjusting power, speed, and focus.
For beginners, most entry-level machines offer guided tutorials, and many have presets for common materials, making the initial learning curve manageable. As you gain experience, you’ll develop a feel for optimizing settings, working with design files, and handling different materials, so it becomes easier to create more complex designs and achieve professional results.
In short, it’s accessible for newcomers and offers plenty of depth for more advanced users.
How does laser engraving work?
A laser engraver works by directing a focused beam of light onto a material’s surface, either to engrave, cut, or mark it. Here’s how it happens in a few steps:
Laser Beam Generation: Inside the laser machine, a laser tube (often CO₂ or fiber) generates a high-energy light beam.
Focusing the Beam: The beam is focused through a series of mirrors or a lens, concentrating it to a fine point on the material.
Material Interaction: The intense energy heats, vaporizes, or removes the surface of the material. For engraving, it removes a thin layer; for cutting, it penetrates all the way through.
Movement and Precision: The machine’s software-controlled motors move the laser along specific paths in the design file, allowing for precise details.
Depending on the power and speed settings, the laser engraver can produce various effects, from shallow etching to deep cuts. Different materials require different laser settings to achieve the best results without damage or unwanted burns.
What laser is used for engraving?
CO2 Lasers
Often used for engraving versatile non-metallic materials like wood, glass, acrylic, leather, and some plastics. Their wavelengths (typically around 10.6 micrometers) make them ideal for organic materials, offering deep and clear engravings. CO2 lasers are popular for hobbyists and businesses alike due to their versatility.
Fiber Lasers
Best for metals and some hard plastics. With a shorter wavelength (around 1.06 micrometers), fiber lasers are excellent for engraving metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and gold. They produce detailed engravings and are widely used in industrial settings for parts marking, tools, and jewelry.
UV Lasers
UV lasers are especially suited for engraving delicate or heat-sensitive materials such as plastics, glass, and some metals with thin coatings. The shorter wavelength allows for a process called “cold marking,” where the engraving effect occurs without significant heat generation, preventing melting or distortion on sensitive surfaces.
Diode Lasers
Typically lower-powered and used for softer materials, such as wood and plastic. Diode lasers are common in hobbyist laser engravers for their affordability, though they may be less effective on tougher materials.
What materials can you laser engrave?
1. Wood
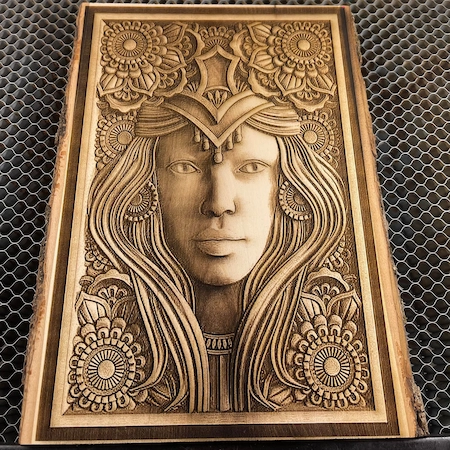



2. Acrylic and plastics
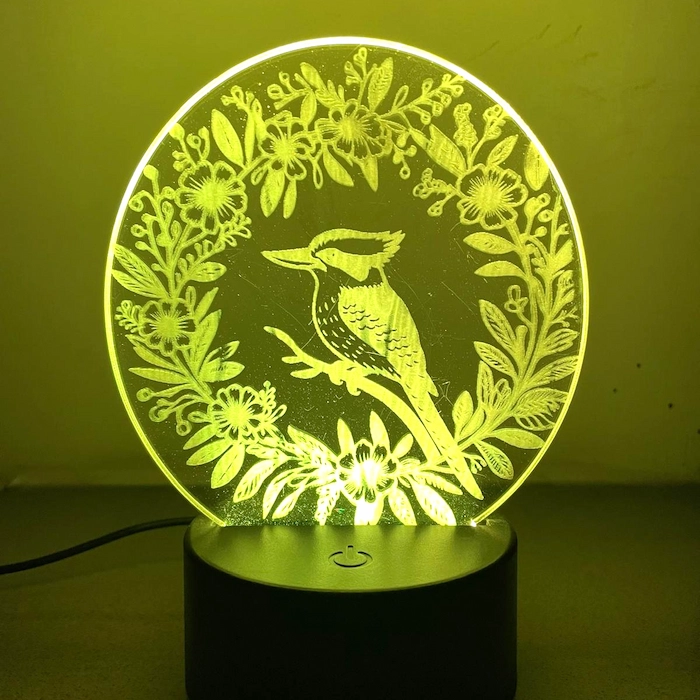
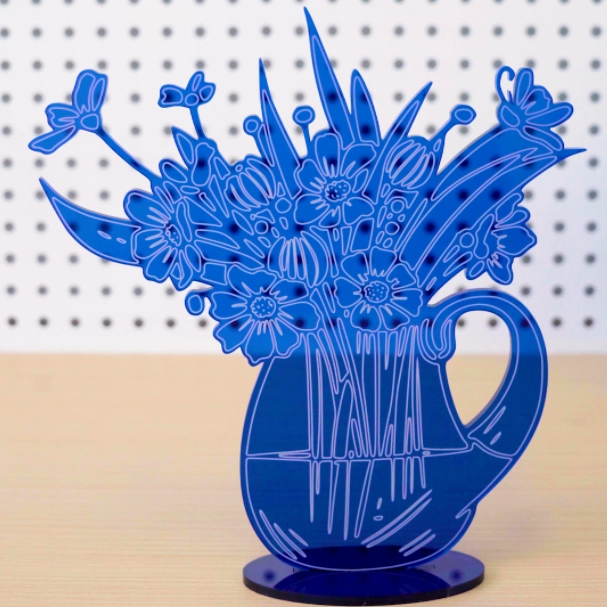



3. Glass
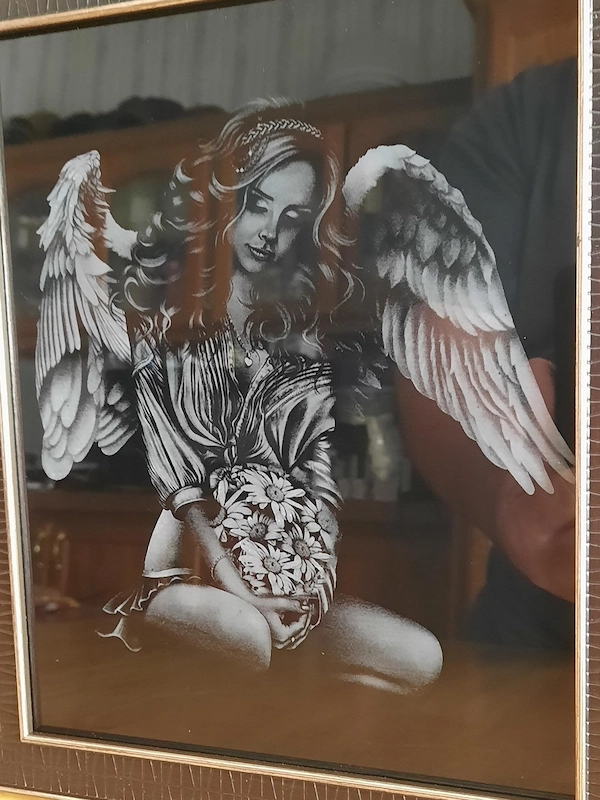



4. Metal



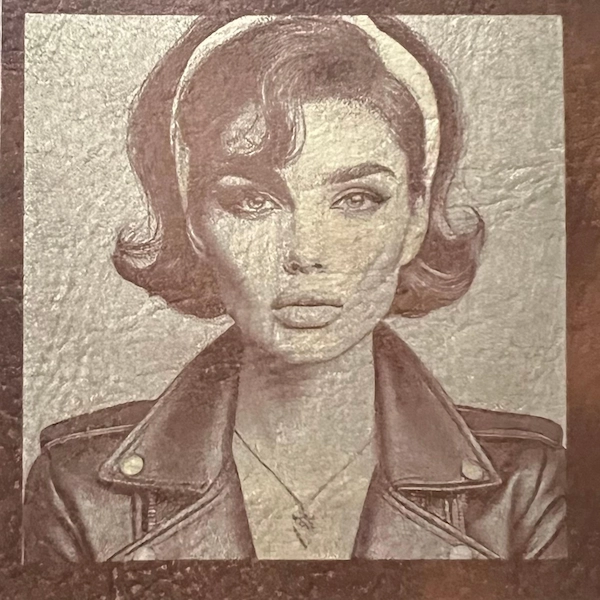
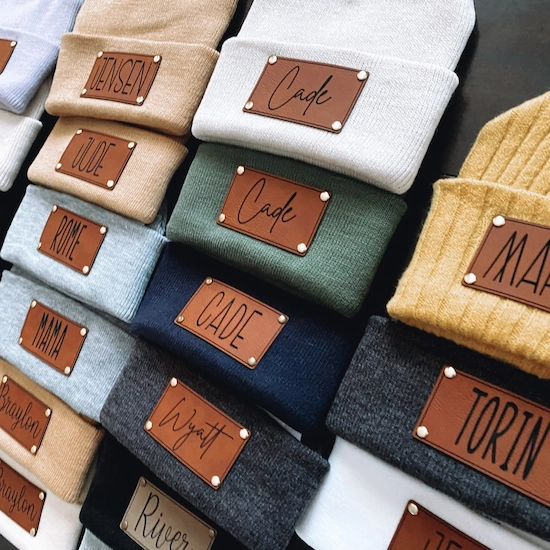
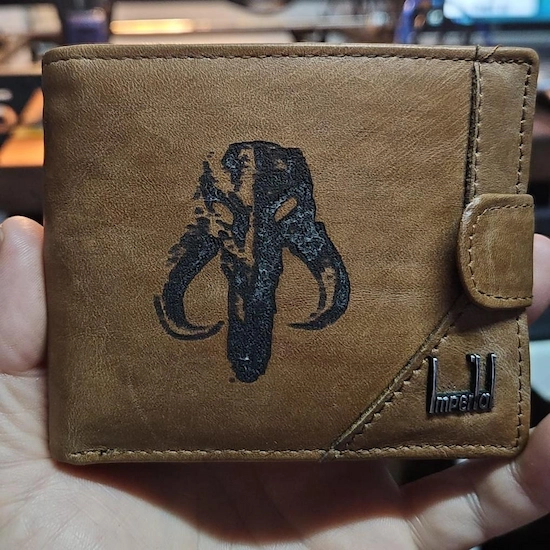
5. Leather



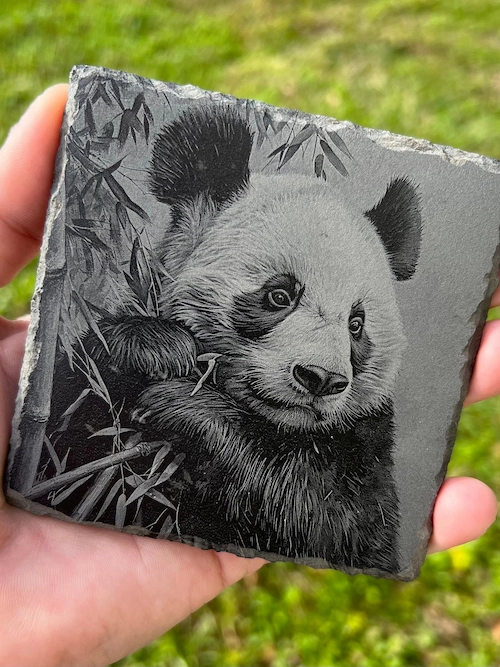
6. Stone
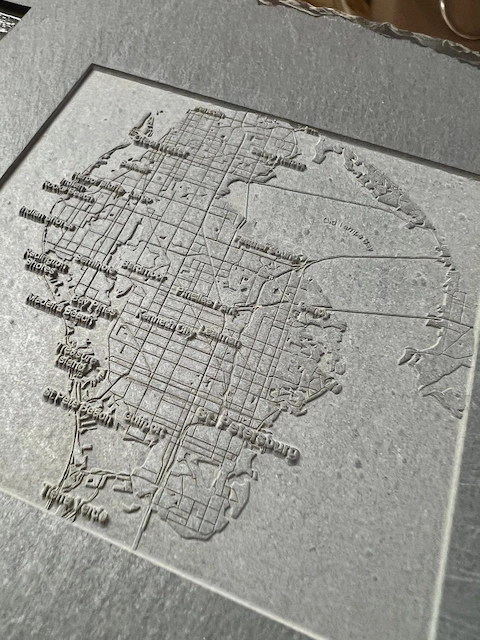


What materials can not be laser engraved?
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
2. Polystyrene (Styrofoam)
3. Fiberglass
4. Epoxy resin
5. HDPE (High-density polyethylene)
6. Artificial leather (PVC-based)
7. Carbon fiber
How to laser engrave?
To start laser engraving, you’ll need a laser engraving machine, design software, and a compatible material for your project. With these essentials, you can bring designs to life by engraving patterns, text, or images onto various surfaces.
1. Prepare your design
2. Select the right material and set up the machine
3. Adjust laser settings
4. Run a test engrave
5. Start engraving
6. Clean the engraved item
Here’s a basic instructional video on CO2 machine operation, showing you how to select files for engraving. You can watch the video to learn, or visit our youtube channel for more information.
Tips and tricks for laser engraving
1. How can you achieve sharper details in laser engraving?
2. What's the best way to minimize material burning?
3. How can you align your design on the material perfectly?
4. How can you make post-engraving cleanup easier?
Is laser engraving dangerous?
Laser engraving can be safe with the right precautions, but there are some risks to consider. Exposure to laser radiation can be dangerous for eyes and skin, so protective goggles or shields are essential. Engraving certain materials may release toxic fumes, so good ventilation or an air filter is important. Additionally, laser heat can create fire risks, especially with flammable materials, so monitoring the machine is recommended.
In a word, with proper safety measures and equipment, laser engraving is manageable and safe.
Other FAQs About Laser Engraving
Q1. How long does it take to laser engrave?
The engraving time depends on factors like material type, design complexity, and laser power. Small, simple designs on common materials can take just a few seconds to minutes, while larger or more intricate designs may require 10-30 minutes or longer. The process also varies by laser type and speed settings.
Q2. How much does laser engraving cost?
Costs vary by material, design intricacy, and whether it’s a DIY job or a professional service. DIY costs may be limited to machine and material expenses, while professional engraving services typically charge anywhere from $5 to $100+ depending on customization.
Q3. How long does laser engraving last?
Laser engraving is durable and generally lasts as long as the material itself, as it’s etched into the surface. On metals, glass, and stone, engravings can endure a lifetime, while on softer materials like wood or leather, longevity depends on use and exposure to elements.
Q4. Is laser engraving a profitable business?
Yes, laser engraving can be profitable, especially for customized products like gifts, signage, and promotional items. Startup costs for a laser engraver are significant, but demand for unique, custom-engraved items often allows for high margins, making it a popular small business option.
- Tags
#laser, #laser engraving, #co2 laser, #fiber laser, #diode laser, #laser machine, #laser engraving machine, #laser engraving materials, #laser engraving cost






.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Česká
Česká
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Romania
Romania
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 ジャパン
ジャパン
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa