Laser Water Coolants & Additives
Overview
Resistivity & Conductivity
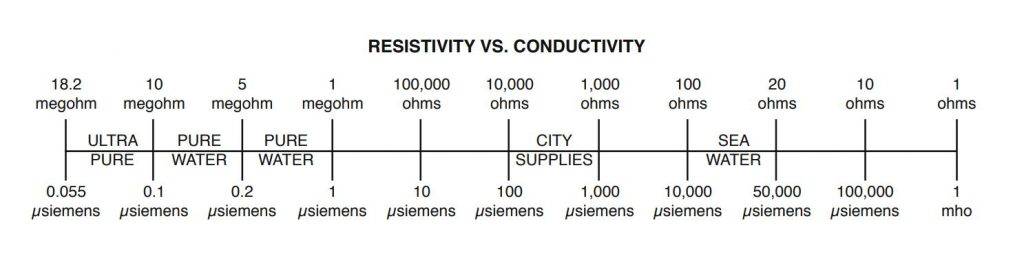
It has been reported, and well documented, that an electrically conductive laser cooling system can and will become charged from the HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) excitation, and resulting population inversion, of the gain medium in a glass tube co2 laser if conditions allow; even if all other peripheral electrical systems are functioning within normal parameters.
And, while the skin effect is not a factor in HVDC transmission, voltages over 10KVDC do exhibit properties that predispose this type of cooling system to certain critical failures. The electrical resistance of an electrical conductor is a measure of the difficulty to pass an electric current through that conductor. The inverse quantity is electrical conductance and is the ease with which an electric current passes.
Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the notion of mechanical friction. The unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (Ω), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S). An object of uniform cross section has a resistance proportional to its resistivity and length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. All materials show some resistance, except for superconductors, which have a resistance of zero. The resistance (R) of an object is defined as the ratio of voltage across it (V) to current through it (I), while the conductance (G) is the inverse:
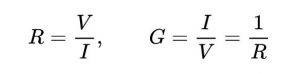
Cooling Fluid Contamination

Common Cooling Fluids
Distilled Water

Tap Water

Tap water’s ability to corrode metal can vary considerably depending on its chemical composition. Chloride, for example, is commonly found in tap water and can be corrosive. Facility or tap water should not be used in liquid cooling loops if it contains more than 25 PPM of chloride.
The levels of calcium and magnesium in the water also need to be considered, since calcium and magnesium can form scale on metal surfaces and reduce the thermal performance of the components. More importantly, ordinary tap water has a conductivity of ~100µS/cm to ~1000µS/cm depending on the contaminants and additives present which is well above the threshold to allow (and even promote) arcing in the tube and allowing the cooling system to become energized.
Deionized Water
As the name implies, DI water has an extremely low concentration of ions which imparts important performance attributes. Firstly it eliminates mineral deposits which block the coolant flow and degrade cooling efficiency. Secondly, it eliminates the risk of electrical arcing due to static charge build-up from the circulating coolant.
The lack of ions in DI water eliminates both of these problems. Deionized water has a conductivity of only ~0.05S/cm. Care must be exercised when using DI water. The very lack of ions also makes this coolant unusually corrosive. Called the “universal solvent,” DI water is one of the most aggressive solvents known. In fact, to a varying degree, it will dissolve everything to which it is exposed. Therefore, all materials in the cooling loop must be corrosion-resistant and compatible with DI water.
Performance Engineered Coolants

Additives
Antifreeze
Automotive Antifreeze

Undiluted Prestone automotive antifreeze (ethylene glycol) has a conductivity of ~633µS/cm. Equal parts of Prestone and distilled water is ~658µS/cm (a 50/50 mix increases conductivity over pure antifreeze by ~4%). A 40-watt co2 tube at ~60% excitation will arc with a coolant conductivity of ~370µS/cm+.
So ethylene glycol can absolutely short down a glass tube (as well as contaminate and degrade the cooling system) and is not recommended for any reason. Moreover, automotive antifreeze is formulated to be safe with vehicle cooling system components but has been reported to degrade nylon and silicone, among other materials, that are common in laser cooling systems.
For instance, nylon is hygroscopic and is moderately attacked by ethylene glycol causing swelling and eventual breakdown while also lowering resistance (and proportionally increasing conductivity). Although, this would only marginally affect overall conductivity since it is above tolerable limits already. The mechanical fatigue would be more concerning with nylon components than the abovementioned electrical characteristics.
RV Antifreeze

RV antifreeze (propylene glycol) on the other hand has an undiluted conductivity of ~414µS/cm and, when diluted equally with distilled water, measures around 200µS/cm. This additive can possibly be used without incident and is recommended as a non-toxic, laser-safe solution to freezing if no other solutions are feasible. This mixture will tend to promote excessive algae growth so an algaecide will also be warranted. As always, it’s better to regulate the temperature of your water with the methods listed at the top of this section.
NOTICE: Since the publication of this article, certain RV Antifreeze has been known to exceed the allowable level of conductivity!
Algaecides & Biocides
Tetra Algae Control

Clorox Bleach

Detergents & Surfactants
Dawn Dishwashing Liquid

Original strength Dawn dish soap is both a detergent and a surfactant that appears to have very little effect on the conductivity of the cooling fluid at any reasonable concentration. Some research has shown that it is not remarkably effective at reducing or eliminating bubbles in the system although I have seen a very slight improvement in my systems.
Knowing just how powerful of a surfactant it is, coupled with the fact that conductivity is not negatively affected in any way, bolsters by reasons for using this additive. The detergence alone must offer some benefit and even if the reduction of air bubbles is not directly benefited I am certain (even without conducting tests) that the dramatic decrease in surface tension and friction must provide better performance. This additive will always get my vote.
WaterWetter

According to their website: “WaterWetter is a unique wetting agent for cooling systems which reduces coolant temperatures by as much as 30 degrees Farenheit. This liquid product can be used to provide rust and corrosion protection in plain water for racing engines, which provides much better heat transfer properties than glycol-based antifreeze.”
While I am sure this is a great product for water-cooled internal combustion engine applications it is a horrible additive for lasers. There are other similar products on the market like MoCool and others which, I’m sure, yield the same results.
Don K. had this to say about this product in his excellent write-up: “I tried adding “WaterWetter” @ 1oz. per 3 gallons. It raised the water conductivity from 4.0µS to 410µS making the coolant unacceptably conductive. The bad part is that it did not remove the bubbles much at all. WaterWetter measured without dilution is very conductive and reads infinity on my meter. Even after I rinsed a bottle that had the wetter in it and then added distilled water it raised the conductivity from 4.0µS to 40µS. The bottle suggests 1oz. per gallon so I was using only 1/3 the amount recommended for car cooling systems.”
I think we can safely eliminate WaterWetter and similar additives from our laser coolant additive list!
Summary
Of course there are users who have cooled their laser with tap water, RV antifreeze, camel urine or whatever. Just because it works for them it isn't a rule to say it works for everyone. How fast a laser cooled with camel urine will fail depends on so much more than the coolant like power usage, how often and how long it´s used, room temperatures, lasing temps of the water and so on. The facts are there, you be the judge of how you want to cool your machine, I can only suggest what to do, or not to do.
The Secret Recipe
- Fill reservoir with 4 gallons of distilled water
- Add 8 drops of Tetra Algae Control freshwater aquarium algaecide
- Add 8 drops of regular Dawn dishwashing liquid
- Stir very gently and energize water pump to fill the cooling system
- Check system for leaks, remove all bubbles and top off with distilled water

.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Česká
Česká
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Romania
Romania
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 ジャパン
ジャパン
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa